Learning Outcomes
i. Identify the key symptoms and signs of drug addiction.
ii. Understand how these symptoms manifest in individuals.
iii. Provide a foundational understanding for recognizing addiction in various contexts.
i. Symptoms of Drug Addiction
Drug addiction symptoms can be physical, behavioral, and psychological, often varying according to the substance used but generally include:
Tolerance: Needing more of the substance to achieve the same effect.
Withdrawal: Experiencing physical and mental symptoms when not using the drug.
Loss of Control: Using more of the substance than intended, or for longer than intended.
Neglecting Activities: Giving up important social, occupational, or recreational activities because of substance use.
Time Consumption: Spending a lot of time obtaining, using, or recovering from the effects of the substance.
Continued Use Despite Problems: Continuing to use the substance even when it causes or exacerbates problems.
Cravings: Having strong desires or urges to use the substance.
ii. Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms may include:
Changes in Appetite: Significant weight loss or gain.
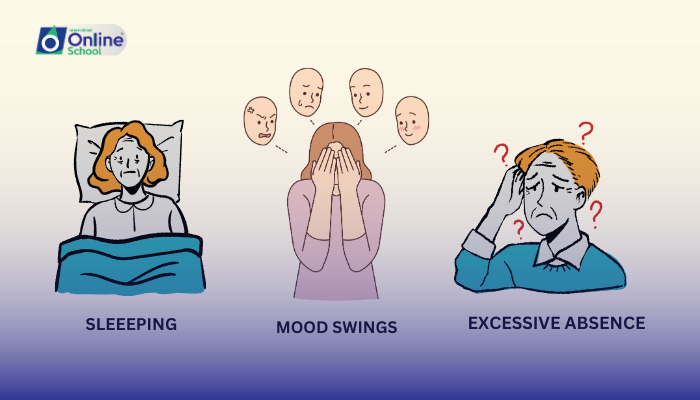
Sleep Disturbances: Insomnia or oversleeping.
Altered Physical Appearance: Neglected grooming, unusual smells, or changes in physical appearance.
Health Issues: Persistent health problems related to substance use, such as liver damage from alcohol or lung problems from smoking.
iii. Behavioral Symptoms
Behavioral signs of addiction can be noticeable:
Secrecy and Deception: Being secretive or dishonest about the extent of drug or alcohol use.
Risky Behavior: Engaging in risky activities while under the influence.
Legal Issues: Encountering legal problems due to substance use.
Relationship Problems: Conflicts with family members, friends, or coworkers.
iv. Psychological Symptoms
Psychological symptoms often include:
Mood Swings: Rapid and severe mood changes.
Irritability and Agitation: Especially when unable to use the substance.
Lack of Motivation: Showing less interest in goals or rewarding activities.
Mental Health Disorders: Exacerbation or development of disorders such as anxiety, depression, or psychosis.
v. Recognizing Addiction
Recognizing addiction involves noticing a pattern of these symptoms that disrupts the individual's life. It often requires a comprehensive approach, considering the context of the individual's life and the severity and duration of symptoms.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of drug addiction is crucial for the timely intervention and support of individuals struggling with substance use disorders. The manifestation of addiction can be complex, involving a combination of physical, behavioral, and psychological symptoms that negatively impact an individual's life and well-being. Acknowledging and understanding these signs are the first steps towards seeking and providing appropriate treatment and support.